Ankle Surgery
Overview:
- Performed to treat severe injuries, deformities, arthritis, or conditions that do not respond to conservative treatments.
- Types of ankle surgery vary based on the underlying condition.
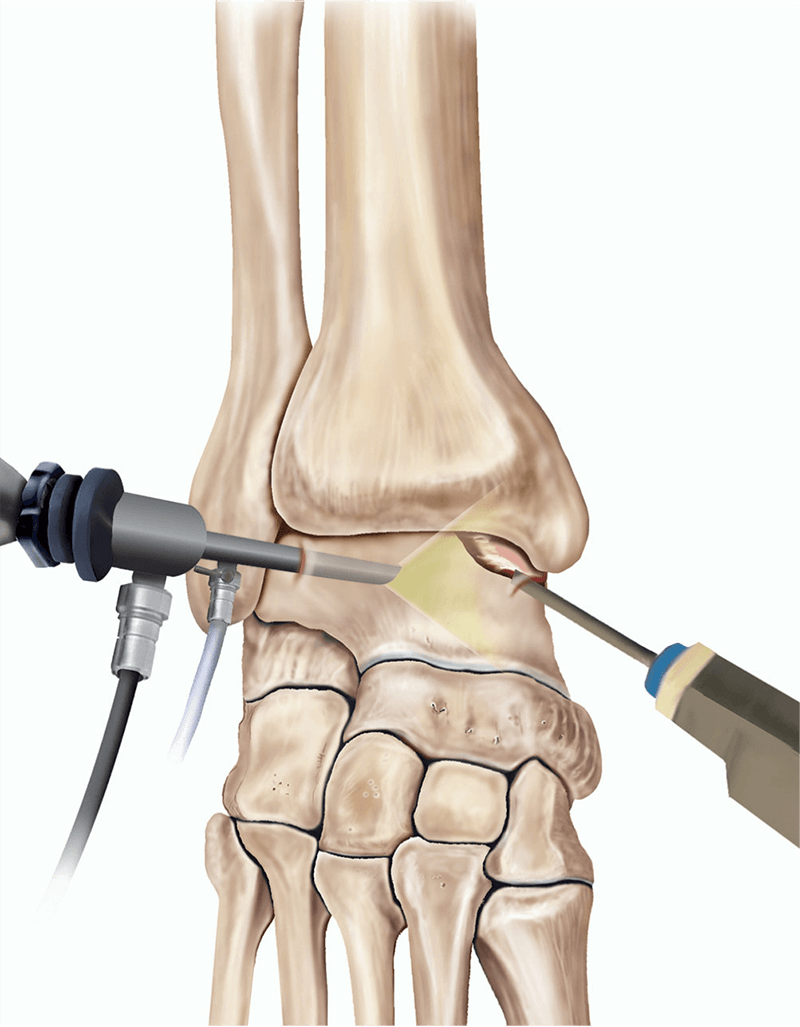
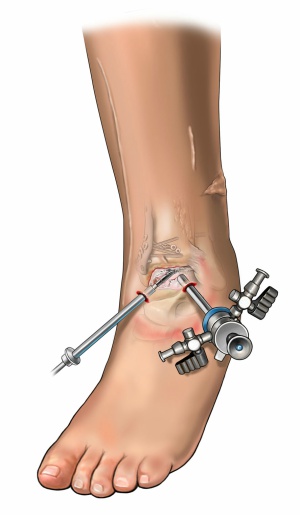
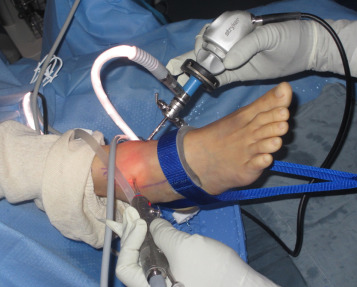
Ankle Arthroscopy
Overview:
- Minimally invasive procedure using a small camera (arthroscope) and instruments to diagnose and treat joint problems.
- Performed through small incisions around the ankle.
Common Conditions Treated with Arthroscopy
1. Osteochondral Lesions:
- Damage to cartilage and underlying bone.
- Treated by debridement, drilling, or cartilage transplantation.
2. Synovitis:
- Inflammation of the joint lining.
- Treated by removing inflamed tissue (synovectomy).
3. Ankle Impingement:
- Pain caused by soft tissue or bone pinching.
- Excess tissue or bone spurs are removed.
4. Loose Bodies:
- Fragments of bone or cartilage in the joint.
- Removed arthroscopically.
5. Ankle Instability:
- Ligament repairs or augmentations can be performed arthroscopically.
Advantages of Arthroscopy
- Smaller incisions and minimal scarring.
- Reduced pain and swelling.
- Faster recovery compared to open surgery.
- Outpatient procedure in most cases.